23/11/2018
Astronomers led by IEEC reveal a cold super-Earth around Barnard’s star
Astronomers led by IEEC reveal a cold super-Earth around Barnard’s star
As mentioned last week in our news about the important discovery made by CRAG’s researchers that have obtained plants more resistant to water scarcity, Barcelona Synchrotron Park (BSP) surrounding area is certainly the park’s prime value offered to its companies.
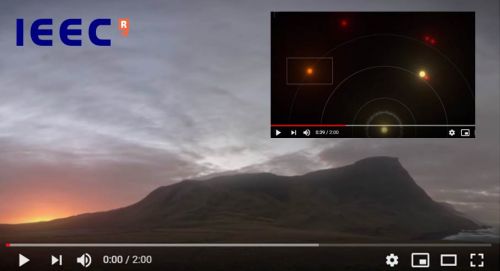
This environment is made of a dense business fabric and the leading research centres of the neighbouring BSP’s Autonomous University of Barcelona (UAB) partner, including CRAG or the Institute of Space Studies of Catalonia (IEEC) from which an international team of astronomers led by Ignasi Ribas of IEEC and Institute of Space Sciences (ICE, CSIC) has found a candidate planet in orbit around Barnard’s star.
Barnard’s star is the closest single star to the Sun and second only to the Alpha Centauri triple stellar system. The team used about 18 years of observations and combined them with new observations with the CARMENES planet-hunter spectrograph at Calar Alto/Spain and other facilities.
Astronomers obtained significant evidence of a planet with mass just over 3 times the Earth’s mass orbiting the red dwarf star every 233 days. This result published last week in the journal Nature would place the super-Earth near the so-called snow-line of the star, where it is likely to be a frozen world.
Video here.
This environment is made of a dense business fabric and the leading research centres of the neighbouring BSP’s Autonomous University of Barcelona (UAB) partner, including CRAG or the Institute of Space Studies of Catalonia (IEEC) from which an international team of astronomers led by Ignasi Ribas of IEEC and Institute of Space Sciences (ICE, CSIC) has found a candidate planet in orbit around Barnard’s star.
Barnard’s star is the closest single star to the Sun and second only to the Alpha Centauri triple stellar system. The team used about 18 years of observations and combined them with new observations with the CARMENES planet-hunter spectrograph at Calar Alto/Spain and other facilities.
Astronomers obtained significant evidence of a planet with mass just over 3 times the Earth’s mass orbiting the red dwarf star every 233 days. This result published last week in the journal Nature would place the super-Earth near the so-called snow-line of the star, where it is likely to be a frozen world.
Video here.
More news
09/12/2014
ADAM involved in the project of shared DC between Malaysia and Catalonia
02/12/2014
ESADE, 4th best business school in Europe
25/11/2014
Nanoparticle technology triples the production of biogas
13/11/2014
A little piece of SENER on comet 67P
05/11/2014
New catalysts investigated with the ALBA Synchrotron
04/11/2014
SENER hosts a meeting with ESA, NASA and ROSKOSMOS in its offices in BSP