15/02/2018
ICMAB traps sunlight with superabsorbent nanomaterials
ICMAB traps sunlight with superabsorbent nanomaterials
In renewable energies, increasing efficiency is a key challenge in the production of “photovoltaic” electrons. This includes elaborating materials that can absorb the largest possible sunlight spectrum.
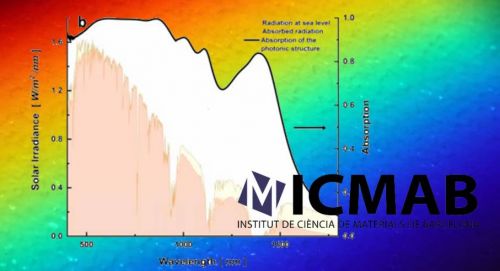
Great news from the Institute of Materials Science of Barcelona (ICMAB), a Barcelona Synchrotron Park’s partner: researchers led by Dr. Agustín Mihi, have created materials that largely absorb a wide range of the solar spectrum, between 400 and 1500 nm (visible light and infrared radiations), using an ultrathin layer of less than 100 nm thick of material.
The followed strategy, low cost and fully scalable, is based on combining the thin layer deposition of semiconductors on metals, and the nanostructuring of the material forming photonic crystals. The obtained superabsorbers materials have many potential applications, especially in the field of photovoltaic energy and photodetection.
Moreover, the researchers provide, in the study published in Advanced Materials, the design guidelines to synthesize other types of materials following the same strategy.
Great news from the Institute of Materials Science of Barcelona (ICMAB), a Barcelona Synchrotron Park’s partner: researchers led by Dr. Agustín Mihi, have created materials that largely absorb a wide range of the solar spectrum, between 400 and 1500 nm (visible light and infrared radiations), using an ultrathin layer of less than 100 nm thick of material.
The followed strategy, low cost and fully scalable, is based on combining the thin layer deposition of semiconductors on metals, and the nanostructuring of the material forming photonic crystals. The obtained superabsorbers materials have many potential applications, especially in the field of photovoltaic energy and photodetection.
Moreover, the researchers provide, in the study published in Advanced Materials, the design guidelines to synthesize other types of materials following the same strategy.
More news
13/12/2017
ALBA Synchrotron Works for People’s Health
01/12/2017
NanoPlastics Awarded As Best Business Idea Of The UAB University Research Park
23/11/2017
The Excellence of Natura Bissé Awarded by Forbes Travel Guide
08/11/2017
SENER, 50 Years in Space and Ambitious Projects Such As the E-ELT Telescope
02/11/2017
The Barcelona Synchrotron Park in the SmartReFlex European project
26/10/2017
New Findings on Malaria Thanks to ALBA Synchrotron