02/06/2016
Mediterranean Corridor: an important infrastructure for Barcelona Synchrotron Park
Mediterranean Corridor: an important infrastructure for Barcelona Synchrotron Park
In the European Union, railway represents 18.4% of the freight transport, 3 times more than in Spain (5.2%).
Carrying out the Mediterranean corridor would be decisive in order to increase the Spanish percentage in favor of this sustainable way of transporting goods (less pollution, less CO2, less accident than for trucks).
This international European gauge railway corridor aims to connect the port of Cadiz (south of Spain) with the port of Barcelona (north), via the ports of Malaga, Almeria, Valencia, Tarragona etc., before continuing to France and the rest of Europe. This railway, which would link all the Mediterranean Spanish border regions, would connect 48% of the Spanish population, 44% of its GDP, 49% of its importations and 51% of its exportations.
This railway corridor is one of the key elements of the Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T) designed in Brussels. In order to accelerate its execution, the Catalan government has recently created a table, the so-called Mediterranean Corridor Strategic Table that includes a 5.6 billion Euros investment just in Catalonia.
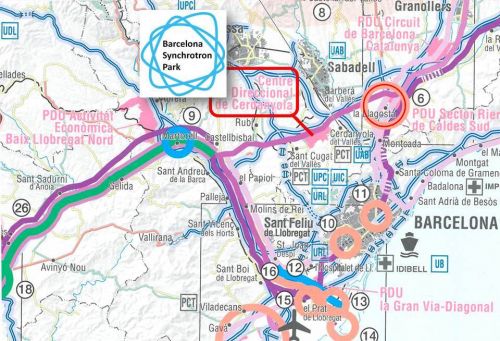
Among the different documents (in Catalan) prepared for this table (all data included in this news were taken from them), a map details the Mediterranean corridor in Catalonia. As far as Barcelona is concerned, it can be seen (see image) that one of the corridor section leaves from the port, runs along the Barcelona Synchrotron Park (“Centre direccional de Cerdanyol” shown on the map corresponds to the local administrative name of the park) and connects to La Llagosta (20 minutes far from the park) where an intermodal station for trains and trucks will be constructed by 2020 as a priority infrastructure.
Very good news for Barcelona Synchrotron Park, its territory and its companies.
Carrying out the Mediterranean corridor would be decisive in order to increase the Spanish percentage in favor of this sustainable way of transporting goods (less pollution, less CO2, less accident than for trucks).
This international European gauge railway corridor aims to connect the port of Cadiz (south of Spain) with the port of Barcelona (north), via the ports of Malaga, Almeria, Valencia, Tarragona etc., before continuing to France and the rest of Europe. This railway, which would link all the Mediterranean Spanish border regions, would connect 48% of the Spanish population, 44% of its GDP, 49% of its importations and 51% of its exportations.
This railway corridor is one of the key elements of the Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T) designed in Brussels. In order to accelerate its execution, the Catalan government has recently created a table, the so-called Mediterranean Corridor Strategic Table that includes a 5.6 billion Euros investment just in Catalonia.
Among the different documents (in Catalan) prepared for this table (all data included in this news were taken from them), a map details the Mediterranean corridor in Catalonia. As far as Barcelona is concerned, it can be seen (see image) that one of the corridor section leaves from the port, runs along the Barcelona Synchrotron Park (“Centre direccional de Cerdanyol” shown on the map corresponds to the local administrative name of the park) and connects to La Llagosta (20 minutes far from the park) where an intermodal station for trains and trucks will be constructed by 2020 as a priority infrastructure.
Very good news for Barcelona Synchrotron Park, its territory and its companies.
More news
13/04/2023
Panattoni acquires 60,000 sqm land plot to build a data center
16/09/2021
Battery technology in the Barcelona Synchrotron Park environment
06/09/2021
Advances in the creation of a state-of-the-art microscopy platform at the Alba Synchrotron
22/07/2021
IBM, the big blue of technology at the Barcelona Synchrotron Park
02/07/2021
SENER, cutting-edge engineering and technology in the Barcelona Synchrotron Park
11/06/2021
Parc de l'Alba: first injection of landfill gas into the distribution network